With the development of China's automobile industry, the manufacturing level of automotive molds has also been improved with each passing day. In the production of automobiles, almost all types of molds have been involved, such as cold die, hot forging die, cold die, hot die, die-casting die and casting die (see Table 1), so the car is made to the die. The demand is particularly large. For an automobile company, with the in-depth development of the market economy, the original 30-year model has been changed to a few models in a year. Generally, the modification of medium-sized trucks requires more than 4,000 sets of molds and weighs 2000 tons. Mold costs have accounted for 15% to 30% of product costs, and its total output value has surpassed the machine tool industry in industrialized countries. The improvement of vehicle quality, the improvement of production efficiency, the reduction of cost, and the speed of product replacement depend to a large extent on the manufacturing precision and quality of the mold, manufacturing cycle, production cost and service life. Therefore, some people say that the mold is the basis for the development of the automobile industry, and it is a sign that the automobile manufacturing industry is maturing.
The basis for supporting the development of the mold manufacturing industry is the mold material industry. In recent years, with the introduction and improvement of technology, the development of mold materials has been extremely rapid. The average annual growth rate of China's major mold steel mills is 12%. From 11 years to 1986-1997, the output increased from 48,800 tons to 113,000 tons. Compared with foreign countries, its development rate can be comparable. In addition, the variety is also increasing, the commonly used mold materials are made in China, and most of the mold materials that are not commonly used can also be produced in China. This has provided strong support for the development of the automotive industry. The consumption ratio of domestic die steel in various industries in 2005 is shown in Table 2. The service life of various types of molds is shown in Table 3.

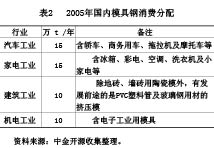
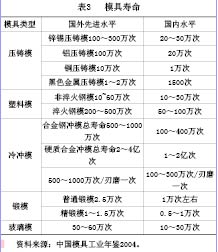
The key process heat treatment technology for mold manufacturing has also developed from the original low level to the international level. Such as vacuum quenching technology, induction hardening technology and laser quenching technology, etc., have been widely used and developed. The surface treatment process after heat treatment has also been greatly improved, such as PVD, TD, nitriding, liquid carbonitriding and spraying, which have been greatly improved and improved. Welding technology has also been widely developed in the field of mold making. Although the mold manufacturer has greatly improved the quantity and quality of the products, it is still far from the development of the automotive industry. For example, most mold companies cannot deliver on time, the quality of the mold is not good, etc. The underlying reason is in mold manufacturing. There are many uncontrollable factors, especially mold materials and heat treatment techniques.
Due to the globalization of technology brought about by economic globalization, the technical level of domestic-funded enterprises, foreign-funded enterprises and foreign-funded enterprises are high and low. Therefore, most of our situations today cannot be divided into domestic or foreign countries, and we must look at the development of the mold industry from the whole world. .
I. Development status of mold materials for automobile manufacturing
With the development of automobile manufacturing technology, the working conditions of molds are increasingly demanding, and the requirements for the performance, quality and variety of molds are constantly being raised. For this reason, countries around the world have actively developed various characteristics in recent years. New mold steel and cast iron that meet different requirements, and have done a lot of work in variety, quality, production process and production equipment, and made great progress.
1. High-speed development and serialization of die steel
Plastic mold steel can be divided into: according to its performance and use conditions:
(1) Small-size mold steel, medium-carbon quenched and tempered steel.
(2) Steel for large and medium molds, pre-hardened medium carbon low alloy steel.
(3) Sulfur-containing, lead and pre-hardened free-cutting die steels for improved cutting performance.
(4) Ageing steel and maraging steel. Used to make complex, precise and smooth molds.
(5) Highly hardenable cold work and hot work die. Used to manufacture integral quenching dies.
(6) Carburized plastic molds.
(7) Corrosion resistant plastic molds.
(8) Mirror polishing mold.
2. Developed advanced cold and hot work die steel
The general cold work die steel is divided into three categories: low alloy cold work die steel, such as 9CrWMnV, medium alloy cold work die steel Cr5Mo1V and high alloy cold work die steel Cr12Mo1V1. In addition, the following new cold work die steels have been developed:
(1) High toughness and high wear resistance cold work die steels such as 8Cr8Mo2V2Si, Cr8Mo2VWSi in the US, QCM8 (8Cr8Mo2VSi), DC53 (Cr8Mo2VSi), TCD (Cr8V2MoTi), etc. in Japan. The advantages of this type of steel are many. The carbides in the structure are fine and diffuse, the bending strength is high, the fracture toughness, wear resistance, machinability, grindability and tempering resistance are good, and the heat treatment deformation is small, which can be developed in the future. Become a general-purpose mold steel.
(2) Flame quenching cold work die steel 7CrMnSiMoV is most commonly used, in addition to Japan's SX5 (Cr8MoV), the United States' CC#1 and so on. It is characterized by a wide range of quenching temperatures, high hardenability and easy flame quenching.
(3) Powder metallurgy cold work die steel Powder metallurgy method can produce ultra-high carbon, high alloy (especially high vanadium content), high wear resistance die steel and carbon-based titanium carbide which are difficult to produce by conventional processes. For example, X320CrVMo135 in Germany, wC>3%, wV>5%, the area of ​​fine and dispersed carbides is 50%, and its life is higher than that of cemented carbide molds.
The development of hot work die steel is also very fast. The three types of general-purpose hot work die steels are: the low alloy hot work die steels are 5CrNiMo and 5CrMnMo; the medium alloy hot work die steels are 4Cr2MoVNi, H11 (4Cr5MoSiV), H13 (4Cr5MoSiV1), H12 (4Cr5MoWSiV) and H10 ( 4Cr3Mo3SiV1); The most widely used high alloy hot work die steel is H21 (3Cr2W8V). In addition, a series of high-performance hot work die steels have been developed, mainly in the following categories:
(1) The chemical composition of the base steel base steel corresponds to the chemical composition of the high-speed steel matrix structure after quenching, so the amount of eutectic carbide remaining after quenching is small, and the carbide is fine and dispersed after tempering, and the toughness of the steel And thermal fatigue performance is good. Such as the United States Vasco MA.
Next page