Example 1, why is the hardness of the 10mm reamer quenching layer low? 1. Tips for the problem (1) In late March of the year, a batch of reamer (998 pieces) was heat-treated and quenched, the material was 9Si Cr, the finished product specification was 10 mm, the retained grinding amount was 0.3 mm, and the heat treatment required hardness was 63-66 HRC. After normal process quenching, the hardness is low. Later, the quenching temperature was increased to 885 °C, and the hardness of the outer part of the blade and the shank was still unsatisfactory. After many tests, the production task could not be completed. (2) In June of the same year, another 966 pieces of 10mm reamers were transferred. Two of the parts were tried and the hardness was only 53 HRC, which was still unqualified. The material was tested by a light bar and the hardness was not qualified. 2. Cause analysis (1) Checking the source of raw materials The batch of 9SiCr material is supplied by a steel mill in Northeast China with a specification of 11mm. The delivery condition is cold-drawn 11 grade and brightly annealed, totaling 20 bundles, with a total weight of 2.68t. (2) Chemical analysis of the chemical composition of the steel, the chemical analysis of the metallized product of 10.3 to 10.1mm is carried out, and the surface carbon content is unqualified (see Table 1). (3) The total decarburization layer thickness of the batch of materials (mm) 9SiCr material unilateral total decarburization layer (ferrite + transition layer) thickness, GB 1299-1985 specified not more than 0. 42 mm, qualified by the steel mill The certificate is 0. 08 mm, the user's metallographic analysis report is 0. 45 ~ 0. 65 mm, the metallographic photograph is 0. 6mm, it can be judged that the total decarburization layer thickness of the batch of materials is unqualified. (4) Quenching hardness test The quenching hardness test selects three kinds of process schemes. Each process plan selects 5 pieces of reamer for hardness test, and takes the average value. The results are shown in Table 2. (5) Metallographic analysis Figure 1 shows the decarburization structure of the raw materials. The surface of the fully decarburized layer is: white is ferrite, the thickness is 0. 20mm; the central part of the decarburization layer is: white ferrite + flaky pearlite + spherical pearlite, thickness is 0. 40 mm; The decarburization zone is: three-level spherical pearlite normal tissue. Figure 2 shows the quenched structure. The surface full decarburization layer is: white is ferrite, the quenching hardness is extremely low; the central part of the decarburization layer is: low carbon martensite + carbide + residual austenite. The undecarburized zone of the heart is: quenched martensite + granular carbide + retained austenite. Through the above analysis and test, the surface carbon content, decarburization layer thickness, quenching hardness and metallographic structure of the 11mm 9Si Cr material were unqualified. 3. Treatment (2) For the work-in-process that has been cut off, the decarburized layer is ground and replaced with a small-sized product. (3) Products that have been quenched and cannot be salvaged shall be disposed of according to the unqualified surface of the raw materials. 4. Improvement measures (1) Further revision of the standards for the re-inspection of metal materials into the factory. Next page 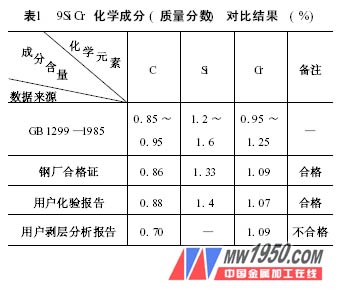
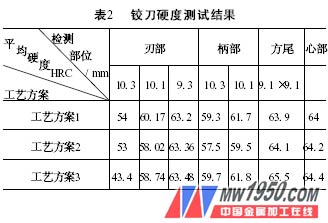
It can be seen from Table 2 that the hardness of the three knives of the reamer blade grinding to 9. 3mm, the square tail, and the core are all qualified, and the other reamer surface hardness is unqualified. 
(1) The surface quality of the batch of raw materials is unqualified, and the procurement personnel contact the steel mill for treatment.
(2) Improve the business level of chemical analysis and metallographic analysts.
(3) It is necessary to strictly prevent oxidative decarburization during heat treatment.