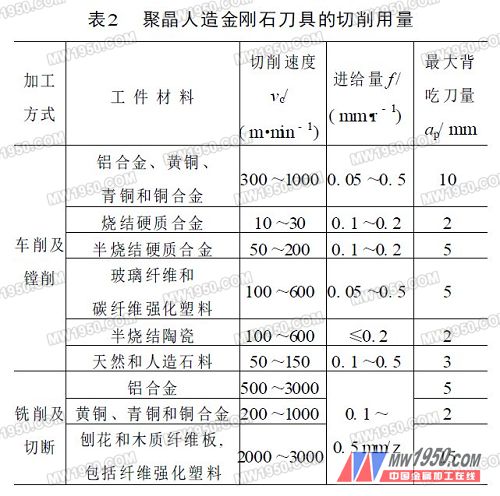
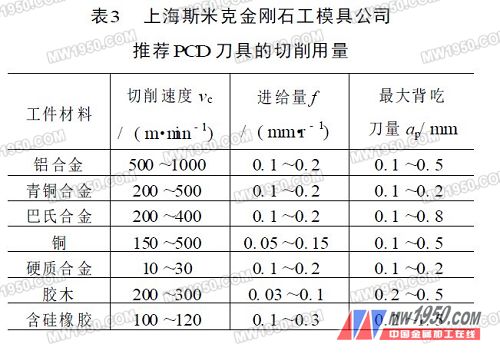
Due to the high brittleness of the diamond material, in order to enhance the cutting edge strength, it can achieve a small surface roughness value, usually the front angle of the turning tool is γo=0°~10°; if the diamond tool is used to cut the aluminum alloy and the copper alloy, γo =0°~20°, the back angle αo=5°~15°. In order to improve the strength of the cutting edge, the negative chamfer is often ground on the cutting edge. The width of the chamfer can be br1=0.1~0.3mm, and the front angle of the chamfer is γo1=-6°~-20°; the tip of the blade needs to be properly rounded and rounded. r ε = 0.2 to 0.8 mm. However, the larger the radius of the tool nose and the negative chamfer, the greater the cutting force and the greater the chance of chattering. Therefore, when the system rigidity of the machine tool-clamp-tool-workpiece is insufficient, especially when machining an elongated workpiece, it is not appropriate to use an excessive tool nose radius and a negative chamfer. High-speed machining (vc>700m/min) high-silicon aluminum alloy with PCD indexable face milling cutter, often adopting positive and negative rake angle, that is, the front anterior angle γp is positive and the side rake angle γf is negative. It can enhance the strength of the cutting edge and is not easy to chip, and can obtain good surface quality and high productivity. 3. Reasonable use of diamond tools (1) Correct selection of the PCD inserts of different varieties and grades of the blade, due to their different composition, the cutting performance is very different, so pay attention to the selection. At present, PCD blades are not classified internationally like cemented carbide. Each production plant has its own varieties and grades. When using it, it must be selected according to the manufacturer's product samples. The commercial particle size of PCD is roughly classified into three types: coarse crystal grains (average size of crystal grains of 20 to 50 μm), medium crystal grains (10 to 20 μm), and fine crystal grains (2 to 10 μm). The larger the grain size, the better the wear resistance, the higher the tool life, but the poor quality of the cutting edge makes it difficult to make a high-precision tool. On the contrary, fine-grained tools have good cutting edge quality and good surface quality. Therefore, at present, the crystal grains of the polycrystal are continuously refined, and there are fine crystals of 1 μm or even 0.5 μm or less, and crystal grains of different sizes are required according to different process requirements such as roughing and finishing. However, Chinese scholars have confirmed that polycrystalline crystal tools have the characteristics of “multi-point cutting and single-point forming†in micro-cutting. Therefore, as long as certain technological measures are taken, coarse-grained (70-30 μm) polycrystalline cutting tools are also used. Can cut out ultra-precision machined surfaces. (2) Select the appropriate cutting amount According to the information provided by the International Society of Production Engineering (CIRP), the recommended cutting amount of PCD tools is shown in Table 2. Table 3 shows the cutting amount of polycrystalline synthetic diamond (PCD) tools recommended by Shanghai Smick Diamond Tooling Co., Ltd. 4. Application effect of diamond cutter Diamond tools solve many machining problems that are difficult to solve in production, and have changed the traditional machining process. Currently, they are used in machinery, metallurgy, mining, automobiles, tractors, bearings, pumps, transportation, energy, precision instruments, aerospace, etc. Used in the industry, significant economic benefits have been achieved. For example, Changchun FAW Group Corporation uses PCD tools to fine-tune the piston pin hole of high silicon aluminum alloy material (vc=160m/min, f=0.08~0.10mm/r, ap=0.05mm), and the tool life is up to 42,500 pieces. 90 times of cemented carbide tools, the surface roughness of the machined surface is reduced from Ra = 0.8 ~ 0.4μm to Ra = 0.4 ~ 0.2μm. Each shift can also reduce the auxiliary time of the tool, 30min, and distribute it to each workpiece. Tool costs are also 85% lower than carbide tools. Machine tools that use PCD tools must have high stiffness, high power, and high speed so that the performance of the diamond tool material can be fully utilized and good economics can be achieved. In addition, the accuracy of the machine tool is good, and the fixture and clamping device for clamping the workpiece must be highly reliable, so as to avoid vibration during machining and damage the tool. It must be pointed out that many of the current machine tools in production cannot meet the processing requirements of PCD tools, so their potential has not been fully utilized. In the future, with the increasing use of high-efficiency equipment such as CNC machine tools (NC) and machining centers (MC), The use of PCD tools will be further promoted. For more articles, please refer to "Metal Processing" Cold Processing 2008 No. 1 Previous page Surgical Head Cap,Medical Scrub Caps,Surgical Hood Cap,Surgical Caps Online Ningbo Autrends Prevention Products Co., Ltd , https://www.autrendsafety.com
2. Tool geometry parameters