1 Introduction Figure 1 Schematic diagram of part of the unequal gap joint structure 2. Joint design that reduces weld defects and residual stress Next page Industrial Model,Model Industrial,Industrial Scale Models,Building Construction Model Nanjing Great Century Art Model Co., Ltd. , , https://www.dsjysmx.com
The polycrystalline diamond compact consists of a PCD layer and a cemented carbide substrate. The PCD layer has high hardness and the cemented carbide substrate has good toughness. The combination of the two makes the PCD composite sheet have excellent cutting performance, so it has been widely used in the industries of metal cutting and drilling.
The polycrystalline diamond compact sheet brazing process is the key technology for manufacturing polycrystalline diamond tools. The cemented carbide substrate of the polycrystalline diamond composite sheet has poor wettability to the brazing material, and has a large difference in thermal expansion coefficient from the 45 steel arbor, which is liable to cause welding stress, resulting in desoldering and difficulty in ensuring welding quality. Brazing of cemented carbides is usually carried out using a Mn-based solder with a brazing temperature of about 1000 °C. The heat resistance temperature of the PCD layer generally does not exceed 700 ° C, otherwise it will cause graphitization of the PCD layer and reduce the use performance of the tool after brazing. Therefore, it is necessary to adopt a welding method which can reduce the brazing temperature and ensure the welding strength. At present, the commonly used PCD composite sheet brazing methods mainly include laser welding, vacuum diffusion welding, vacuum brazing, water cooling brazing, inert gas protection brazing, and the like. Although these methods can achieve sufficient welding strength, the investment in welding equipment is large, the operation and maintenance cost is high, the process is complicated, and the production operation is cumbersome, which greatly increases the manufacturing cost of the PCD tool, and is not conducive to the promotion and application of such advanced tools. In this paper, a part of the unequal gap joint structure design is used, using silver-based solder (Ag-Cu-Zn-Cd), and brazing in the air by high-frequency induction heating (brazing temperature 690 ° C). The brazing process is simple in operation, high in production efficiency, low in processing cost, and can ensure brazing quality. 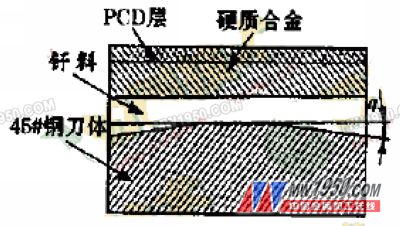
Regardless of the brazing process used, it is generally difficult to completely eliminate brazing defects. The defects such as pores and slag inclusions in the brazing joint are closely related to the melting of the brazing material during the brazing process and the flux cauterization process. In high-frequency induction heating, due to the skin effect and the sharp angle effect, the edge temperature of the 45 steel shank brazing seam is higher than the internal temperature, and the edge brazing material first melts, so that the residual gas and flux inside the brazing seam are very It is difficult to discharge the brazing seam from the narrow parallel gap, so that it is easy to form defects such as pores and slag inclusions in the brazing seam. Since the thermal expansion coefficient of the cemented carbide substrate (a=4.5~7×10-6/K) is different from the thermal expansion coefficient of the 45 steel shank (a=11.65×10-6/K), the two materials are heated when they are heated. In the case of expansion and post-weld cooling, since the solder has firmly joined the two materials and cannot be freely shrunk, residual stress is caused in the material (compression stress at the weld, tensile stress on the PCD surface), and the weld quality is lowered. In order to improve the welding quality, the partial unequal gap joint structure shown in Fig. 1 can be used in actual production to reduce brazing defects and residual stress.
As can be seen from the figure, the intermediate plane ensures the relative positional accuracy between the welding faces, and the gaps on both sides facilitate the discharge of gas and flux. When heating, first fill the middle part of the brazing joint with the brazing filler metal, and then fill the edge part, the gas and slag which are surrounded by the middle part gradually flow to the large gap of the edge with the caulking action of the brazing material, and finally are discharged out of the brazing seam. In addition, a dense joint of the structure can be obtained. At the same time, the gap on both sides can reduce the shrinkage of the 45 steel shank with large thermal expansion coefficient during cooling to alleviate the increase of residual stress. Under the combined effect of the two, the quality of brazing can be greatly improved.