The use of solid-state batteries in space does not sound like anything new. But the problem is that this technology is not yet universal on the planet. Despite this, there are still many start-ups that hope to start battery experiments on the moon as soon as possible. The reason why it is so positive is because it sees a bright future for the exploration of the moon. Private or state-owned institutions such as ispace are racing to send robots and experimental instruments to the moon. However, after arriving at this satellite, it is necessary to consider a backup energy solution that has not been exposed to the sun for a long time. With and without the sun, the moon will experience extreme temperature differences. It is of great significance to the lunar exploration to find a battery that can withstand such temperature fluctuations, but still store energy efficiently. Solid-state batteries may be a promising solution. Compared with ordinary batteries, it uses a solid electrolyte, you can simply think of it as a super version of traditional lithium-ion batteries. To help charged particles move between the two poles of the battery, lithium ions need to rely on a flammable liquid as an electrolyte. Unfortunately, even on Earth, this liquid can cause problems. At high temperatures, the electrolyte may cause the battery to fail and catch fire, or even explode devices such as cell phones. In a low temperature environment, the electrolyte will freeze to a solid, causing the battery to decay significantly. In contrast, the electrolyte in solid-state batteries has been specially designed. Although it is not wrapped with liquid, this solid material can help ions move back and forth. Francesco Pagani, a solid state battery researcher and doctoral student at the Swiss Federal Materials Science and Technology Laboratory, said: Solid-state batteries do not need liquid to wrap everything, but stack different parts into solid layers, and can make the battery more compact. Compared with traditional lithium-ion batteries, solid-state batteries can save more energy and charge faster. Theoretically, it can better withstand the severe temperature difference of the moon, from 260 ° F (127 ° C) under sunlight to -280 ° F (-173 ° C) under shadow. Even if it is overheated, it will not burn or explode easily. Although the charging speed of the solid-state battery will be slower at extreme low temperatures, at least it can survive in the space environment. If you change to a lithium ion battery, there is no need to consider. It is reported that the planned solid-state moon battery will be manufactured by NGK Spark Plug in Japan. Although the exact specifications of this solid-state battery have not been determined, it is known that it will use a ceramic electrolyte (characteristically very stable, so it is extremely popular). At present, it plans to do some fairly basic tests to verify whether the battery can survive and maintain charge in the vacuum environment of the moon. It hopes that this experiment can expand the feasibility of space batteries. C12V280 Engine 6 Series:power Range 2493KWm-3207KWm Engine.2493KWm-3207KWm CCSN POWER GENERATION INC.(Engine is a subsidiary of CCSN) , https://www.ccsnengine.com
(Photo from: ispace) 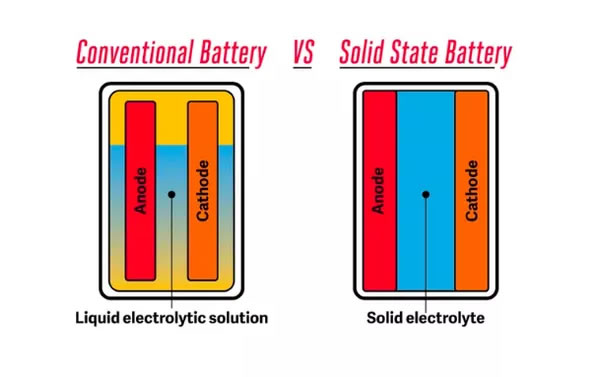
(Photo from: Will Joel / TheVerge)