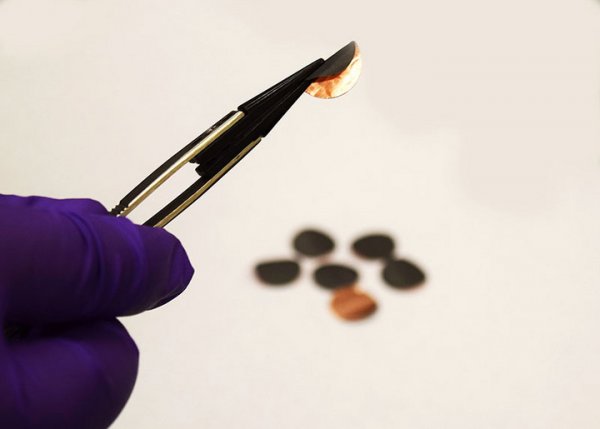
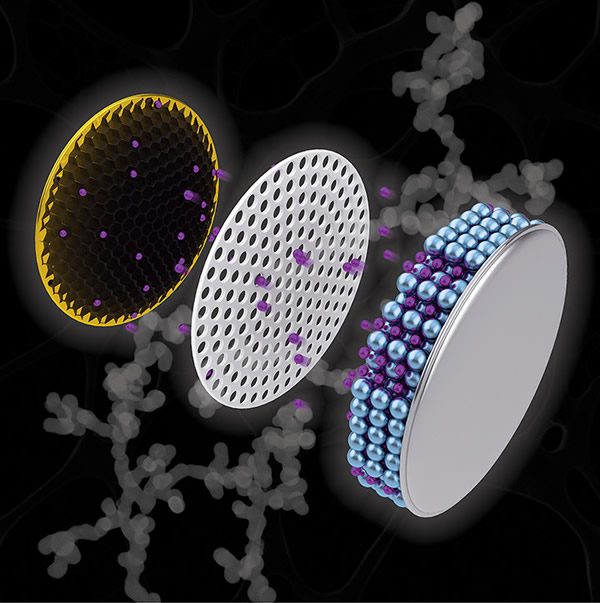
According to foreign media reports, the length of battery life in mobile phones, computers or electric vehicles depends on how much lithium ions can be stored in the battery's negative electrode material. If the lithium ions in the battery are depleted, no current can be generated to drive the device, and the device cannot be used. However, the materials with higher lithium ion storage capacity are either too heavy or not suitable in shape, and cannot replace the electrode material currently used in batteries-graphite. Now, scientists and engineers at Purdue University have introduced a method to reassemble electrode materials and design new electrodes, thereby extending battery life, making batteries more stable, and reducing charging time. The study created a network structure called "nanochain" (nanochain), which is composed of antimony. According to reports, antimony is a metal that can enhance the charging capacity of lithium-ion batteries. The researchers compared such nano-chain electrodes with graphite electrodes and found that when a battery equipped with nano-chain electrodes and coins was charged for only 30 minutes, after 100 charge and discharge cycles, the lithium ion capacity was that of a battery equipped with graphite electrodes. double. Some commercial batteries have begun to use carbon-metal composite materials similar to metal antimony anodes as electrodes, but because this material absorbs lithium ions, it will expand to three times larger than graphite electrodes, causing such batteries to be charged. Has become a safety hazard. Scientists at Purdue University use compounds – reducing agents and nucleating agents to connect small antimony particles into the shape of nanochains to accommodate the expansion space. The special reducing agent used by the research team, ammonia borane, creates voids inside the nanochains, allowing some expansion and preventing electrode failure. The research team applied ammonia borane to several different antimony compounds and found that only the antimony ammonia produced a nano-chain structure, and the nano-chain structure kept the lithium ion capacity of the battery stable after at least 100 charge and discharge cycles. . The researchers said that this battery design can also be used for larger batteries, and the team plans to test it in soft-pack batteries next. Perhaps in the future, batteries suitable for electric vehicles can be developed. (Author: Yuqiu Yun) The new Stainless Steel Wire Rope should not be used immediately under high speed and heavy load conditions, but should be run under low speed and medium load conditions for a period of time, so that the new wire rope can adapt to the use state first, and then the speed of the wire rope can be gradually increased to lift the load. That is, wire ropes must go through an initial break-in stage before high-speed, heavy-duty work.
When using stainless steel wire ropes and pulleys, care must be taken to prevent the wire ropes from jumping out of the pulley grooves. If the wire rope is still used after it is removed from the wheel groove, the wire rope will be deformed, kinked, broken wires, and broken strands. This will seriously shorten the service life of the wire rope. If the rope breaks, it usually has very serious consequences.
Long Link Chain,Galvanized Link Chain,Round Steel Link Chain,Stainless Steel Long Link Chain Jiangsu Hongze Stainless Steel Wire Rope Co., Ltd , https://www.hzrope.com