Steel turning is one of the largest areas of machining and is used in almost all workshops, which means that steel parts are used regardless of material type, workpiece type, process type and batch size. This is mainly used for part machining in the ISO P25 application range. The processing conditions are from good to bad, and it is important to improve the processing performance. Worst environment By increasing production efficiency, improving process safety, and extending the tool's more predictable life, coated indexable inserts offer greater potential for improved production. ISO P25 new generation coated steel turning material developed by Sandvik Coromant GC4325 However, since 1970, the introduction of coated carbide materials, steel parts turning revolutionary progress. Over the years, six generations of P25 materials have been developed, which continuously improve the processing performance and greatly improve the manufacturing efficiency. A wide range of applications can be optimized by using universal steel turning materials. The seventh generation P25 blade material is being upgraded. This new achievement is entirely due to the intensive and extensive development of coated carbide inserts, not only for materials science, but also for application analysis and blade manufacturing processes. When designing new steel turning materials, it is necessary to evaluate and study a variety of factors, including raw materials, hard particle mixtures, binders, particle size, matrix gradient design, and more importantly coating technology. Stainless Steel Sanitary Tubing is the main tubing line for a piping system. Generally, sanitary welded tubings are made in stainless steel 304 and 316l, but we provide other grade too such as hastelloy C22, 316Ti, Titanium and nickel alloy etc. Kaysen offer both sanitary seamless tubes and sanitary welded tubes to ASTM A270, ASTM A249, A269, ASTM A554, DIN11850, and size is up to 12″. Inner and outer surface is polished to meet the high purity requirement of hygienic industries. Kaysen sanitary is ability to supplying qualified sanitary tubings comply to your your condition and FDA,GMP requirement. Sanitary Welded Tubes,Sanitary Tubes ,Stainless Steel Sanitary Tubes,Stainless Steel Welded Pipes Kaysen Steel Industry Co., Ltd. , https://www.chinasanitaryvalve.com
Since the introduction of coated indexable inserts, a blade material has been a common solution for this wide range of applications. The P25 material is continuously improved and processed. This is a general-purpose steel turning material that optimizes a large number of processes.
Today, through the innovation of tool materials, performance has improved significantly, and this innovation has never been more than any similar material upgrade in the past.
The cutting edge of any tool is subject to heat. During the cutting process, while the workpiece material is close to the cutting edge, the knife is first eaten at the main cutting edge. Then, after the main cutting edge, the front knives play a major role in the flow of iron filings. Auxiliary shear planes that transfer a large amount of energy to the material to the yield limit. In steel turning, the combined force is large (1,400 to 3,100 Newtons per square millimeter, depending on the type of steel), and the temperature is high (up to 1,000 degrees Celsius). It is in the iron filing area that the ability to test tool materials determines the main impact of the machining operations.
The combination of the cutting edge groove type and the tool material of the chipbreaker on the indexable insert along the cutting edge line determines the shear stress effect because the chip load on the entire surface is concentrated and then takes away most of the heat generated during processing. . Friction is a major factor, so the texture of the iron filing surface and the blade surface plays an important role in performance.
The wear mechanism of the iron scraping flow area of ​​steel parts is mainly chemical melting, and there is a tendency of partial plastic deformation. Diffusion wear is a major feature of high-speed cutting, as well as abrasive wear, which occurs primarily at the clearance surface of the insert, which is continuously controllable. Steel turning must be continuous and controllable in wear, such as major plastic deformation, hot cracking and groove wear.
Steel turning
Steel turning is the most common processing application in the world and is used in many metalworking workshops. However, due to the use of a variety of materials, from non-alloy steels, low-alloy steels to high-alloy steels, from soft viscous materials to hard-grinding materials, etc., physical properties and conditions are ever-changing. Bars, tubes, forgings, castings, rolling, drawing, untreated, tempered and pre-machined workpieces have different materials and processability levels are significantly different. These are within the scope of ISO P25 applications for steel turning. Taking into account the different wear mechanisms of different steel parts, it is impossible to handle all processing applications with a single blade material. Therefore, it is impossible to use the same processing technology for different types of production in the entire field (either small-scale production in small workshops or mass production in large workshops).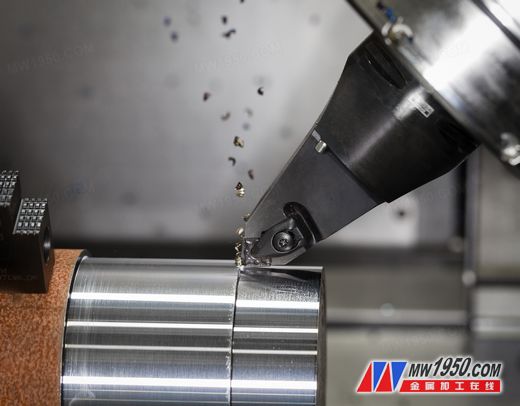 
It is no exaggeration to develop a new generation of P25 blade material for steel cutting, which completely changes the rules of the manufacturing game. This is a major advance in the science of cutting tool materials, meeting the needs of modern production, and overcoming a number of technical difficulties: predictability of tool life, safety of machining, continuity of part quality and higher cutting speed. 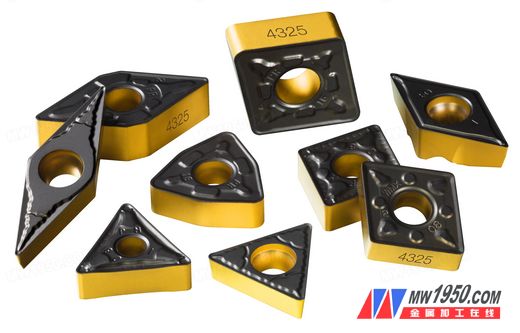
A variety of low-volume or high-volume production optimizations The versatile GC4325 insert geometry, tip radius, insert size and blade shape options offer a new range of optimization possibilities in combination with material selection. This material is a breakthrough innovation in blade coating. With the new edge processing technology and further controllability, the blade base is more robust and more balanced, and the blade post-processing process is further developed, in line with existing R&D approaches and manufacturing factors. coordination.
Why is the new tool material so perfect?
-The blade base is tougher and more balanced - the cutting process uses new processes and new control methods - a new breakthrough in blade coating innovation - further research into post-treatment processes - coordination of all existing factors
The blade base is more resistant to plastic deformation. The cutting edge can withstand higher temperatures without sacrificing performance. The new substrate gradient also suppresses microcracks and improves the durability of the edge line.
To ensure a smoother cutting action throughout the flow area, the geometry and dimensions of the cutting edge are customized. A new breakthrough was made in the alumina coating organization using chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The edge line has better toughness and wear resistance, and is especially suitable for interrupted cutting, which is largely due to the newly developed post-treatment process.
All of this means that the tool material technology has made substantial progress, and combined with the new generation of coated blade technology, it has fundamentally solved the performance problem of turning tools in such a wide variety of conditions and harsh conditions.
One of the main innovations in tool materials is coating organization and adhesion. Of course, as part of the oxide ceramic and proven by practice, alumina is a mature tool material, a mature coating. This is a very effective blade protection layer with chemical inertness, low thermal conductivity, and high resistance to crater wear by diffusion. This material has a melting point above 2000 degrees Celsius and is very hard due to its densely packed crystalline structure.
To date, conventional alumina coatings have a random crystal orientation. These alumina coatings have satisfactory processing properties and can overcome some of the disadvantages caused by the harsh conditions of the edge line and the rake face. Studying the surface, if the actual crystal direction is controllable, many cutting edge characteristics are also controllable, and more importantly, it has been significantly improved.
Stainless Steel Sanitary Welded Tubing-Sanitary Tubing
Material: SS304, SS316L, EN 1.4301, EN 1.4404, etc
OD diameter: 1/2" - 12"
Thickness: 0.5mm - 6mm
Standard: ASTM, JIS, DIN, JIS, SUS, GB
Length: 6m or customer made
Tolerance: OD. ±0.2mm; Thickness: ±0.02mm; Length: ±0.5mm
Surface Treatment: Matt Finish or Mirror Finish (320# 400# 600#) etc
Application: Boiler, heat exchanger, construction, hygienic, pharmacy, power, petrochemical
Strength:
Heat Treatment of solution annealing for the sanitary tubings and fittings are available
High precision on dimension and wall thickness
Both seamless and welded sanitary tubings are available
Length is up to 12 meters.
Min. order quantity of sanitary tubings is from 300Kgs.
Offer industrial pipe and tubes according to order.
PMI test to verify material grade.
Visual and surface 100% examination before shipment.
End protected for shipment.