The power transformer is the main equipment of the power system and is prone to short-circuit faults during long-term operation. Outlet short circuits can cause insulation overheating faults and winding deformation failures, where transformer winding deformation has become a direct cause of other failures and accidents. This article analyzes the short-circuit fault of the transformer and puts forward the remedial measures and technical improvement ideas about the short-circuit fault of the transformer. The short-circuit fault of the power transformer mainly refers to the short circuit at the outlet of the transformer, the short circuit between the internal lead of the transformer or between the windings and the ground, and the fault caused by the short circuit between the phase and the phase of the transformer. According to statistics, export short-circuit faults have the most frequent and severe impact on the normal operation of power transformers, and even more than half of transformer accidents in some regions are directly caused by short-circuit fault current surges, and this situation has increased in many regions. the trend of. Transformer outlet short-circuit fault will bring serious losses to people, especially the fault or accident caused by transformer low-voltage outlet short circuit, usually need to replace some or all of the windings. The short-circuit current causes insulation overheating faults. The main reason is that when the power transformer suddenly experiences a short circuit, the short-circuit current with a rating of several tens of times may be concentrated at the same time through the high- and low-voltage windings, causing it to generate an extremely large amount of heat instantaneously, resulting in serious power transformer failure. fever. Once the overloaded short-circuit current exceeds the capacity of the power transformer, the thermal stability of the transformer is deteriorated, and the insulating material of the transformer is seriously damaged, causing the breakdown or damage of the transformer of the next year. The main short-circuits of the power transformer are three-phase short circuit, two-phase short circuit, two-phase ground short circuit and single-phase ground short circuit. Among them, the single-phase ground fault has the highest failure rate and accounts for more than half of all short-circuit faults. Two-phase short circuit faults are secondary, and the other two short-circuit faults are less likely to occur, but the instantaneous short-circuit current generated by a three-phase short circuit has the highest value. Therefore, the three-phase short-circuit current must be fully considered when designing a power transformer. Short circuit electric power causes winding deformation failure, mainly due to the power transformer in the short circuit impact generated excessive short-circuit current, this situation may even cause the relay protection delay relay action, so that the windings produce more serious deformation Or damage. If the short-circuit current is relatively small, then the relay protection can correctly perform the protective action, and therefore the resulting winding deformation is also very slight, and such minor deformations should be promptly overhauled. If light winding distortion is neglected and the position of the spacer is not recovered in time, the press studs of the winding and the iron yoke pull plate and the tie rod are fastened, and the clamping force of the lead wire is strengthened, after being subjected to multiple short-circuit shocks, the power is The transformer will be damaged due to the accumulation of winding deformation. When the windings are suddenly short-circuited, the current-carrying conductors are subjected to strong electrodynamic forces under the effect of magnetic flux leakage. We decompose this electrodynamic force into the two components of the vertical axis and the horizontal axis. The magnetic field on the vertical axis causes the winding to generate radial force, while the magnetic field on the horizontal axis causes the winding to receive axial force. Therefore, when the winding of the power transformer is short-circuited at the outlet, it needs to withstand large axial and radial electrodynamic forces. The axial electromotive force will compress the winding in the middle. It is a kind of mechanical stress, which greatly influences the insulation characteristics between the winding turns and damages the insulation between the turns of the winding, and the axial force makes the whole winding under tension and pulls in the wire. Extensive stress. The axial force of the winding mainly has two parts: one part is caused by the radial component of the magnetic flux leakage part of the winding end interacting with the current carrying conductor, and acts on the inner and outer windings in the form of pressure; the other part is due to The radial magnetic flux generated by the imbalance of the ampere turns inside and outside the winding is generated by the interaction between the current leakage conductor and the current-carrying conductor. This force causes the inner winding to be squeezed, the outer winding is subjected to tensile force, and the larger the imbalance of the ampoule, the shaft is generated. The greater the force is. The radial direction of the electromotive force is mainly to expand the entire winding outwards, causing it to lose stability and cause interphase insulation damage. If this kind of electrical power is too large, it will lead to more serious consequences such as twisting of windings or breakage of wires. Based on the above, in order to prevent the winding deformation caused by short circuit and other issues, reduce the transformer short-circuit accident rate, the academic community to the power transformer short circuit fault remedial measures were discussed, but also put forward some technical improvements. To reduce the occurrence of power transformer short-circuit accidents, we must first make a good selection of transformers, select transformers that meet the requirements of short-circuit tests, and reasonably determine the capacity and short-circuit impedance of the transformers; second is to optimize the operating conditions of the transformers, mainly to improve the power lines. Insulation level, to reduce the impact and hazards of the near area; the third is to optimize the operation of the transformer, according to the precise calculation of the short-circuit current to determine its mode of operation, while taking certain protective measures to limit the hazard of short-circuit current; To improve the level of operation and management, to avoid short circuit caused by misuse, to strengthen the transformer inspection and maintenance. From the technical point of view, it is necessary to use advanced technologies for improvement, including winding structures, body structures, and core structures.
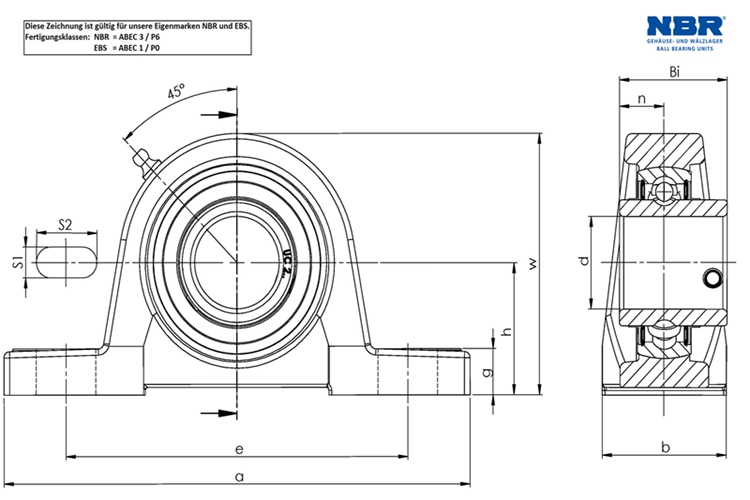
The UCF pillow block mounted bearing series has four bolt holes, and a set screw lock is designed for mounting onto bearing surfaces parallel to the shaft axis, such as conveyor belts. This ready-to-mount unit has solid base cast iron housing, chrome steel bearings, and is designed for efficient operation at a wide range of speeds. This one-piece pillow block housing allows for a stationary outer ring and rotating inner ring. Insert bearing maintains the separation between moving parts to reduce rotational friction, and to support radial and axial loads. The bearing is secured to the shaft with set screws to prevent slippage. This mounted bearing is used in food and beverage manufacturing, textile industry and many other industrial manufacturing.
Pillow blocks are usually referred to the housings which have a bearing fitted into them & thus the user need not purchase the bearings separately. Pillow blocks are usually mounted in cleaner environments & generally are meant for lesser loads of general industry. These differ from "plummer blocks" which are bearing housings supplied without any bearings & are usually meant for higher load ratings & corrosive industrial environments. However the terms pillow-block & plummer-block are used interchangeably in certain parts of the world. Ucf Pillow Bearing,Ucf Pillow Block Bearing,Ucf 207 Flange Bearing,Flange Mounted Pillow Block Bearing Shijiazhuang Longshu Mechanical & Electrical Equipment Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.lsjgbearing.com
However fundamental application of both types is the same which is to primarily mount bearings safely enabling their outer ring to be stationary while allowing rotation of the inner ring. The housing is bolted to a foundation through the holes in the base. Bearing housings are either split type or unsplit type. Split type housings are usually two piece housings where the cap and base can be detached. While certain series are one single piece housings. Various seals are provided to prevent dust and other contaminants from entering the housing. Thus the housing provides a clean environment for the expensive bearings to freely rotate hence increasing their performance and duty cycle.
Bearing housings are usually made of grey cast iron. However various different grades of metals can be used to manufacture the same.