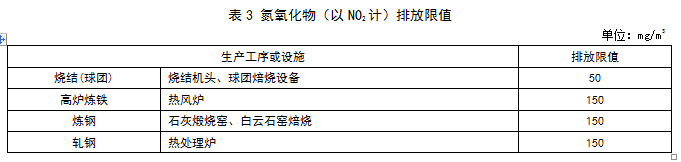
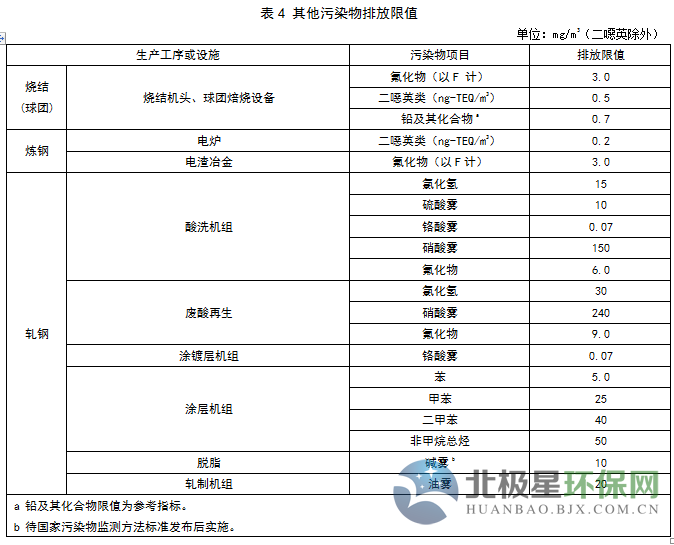
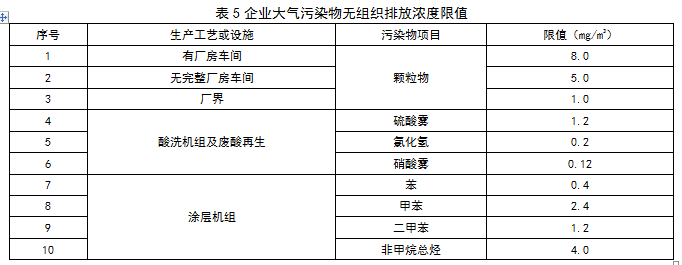
Recently, Hebei issued the "Ultra-low Emission Standards for Air Pollutants in the Iron and Steel Industry (Consultation Draft)". On January 1, 2020, the existing company's sintered pellets will perform 10 mg/m3 of particulate matter, 35 mg/m3 of sulfur dioxide, and 50 mg/m3 of nitrogen oxides. The new enterprise shall implement the emission limits specified in Tables 1 to 4 from the date of implementation of the standard. Specific requirements are as follows: The industry's organized emission standards for atmospheric pollutant emissions are as follows: The existing enterprises shall implement the emission limits specified in DB13/2169-2015 and the “Publication of Hebei Provincial Environmental Protection Agency on the Implementation of Special Emission Limits of Air Pollutants in Hebei Province†(No. 1 of 2016) before January 1, 2020 The emission limits specified in Tables 1 to 4 shall be implemented as of January 1, 2020. The new enterprise shall implement the emission limits specified in Tables 1 to 4 from the date of implementation of the standard. Ultra-low emission standards for industrial air pollutants (draft for comments) Foreword This standard is drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T1.1-2009. This standard is a revision of DB13/2169-2015 "Industrial Air Pollutant Emission Standards". The main contents of this revision: ——Increased method for determining the concentration of atmospheric pollutants in oil mist; ——Adjusting the concentration limits of particulate matter, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides in the sintering (pellet), blast furnace ironmaking, steel making and steel rolling processes; ——Adjusting the emission limit of the sintering head, the fluoride in the pellet baking equipment, the dioxins in the electric furnace and the concentration of the atmospheric pollutants in the electroslag metallurgical fluoride; Chapters 4 and 5 of this standard are mandatory. This standard was drafted: Hebei Zhonglian Energy Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd., Hebei Huanxue Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd., Hao Group Co., Ltd. The main drafters of this standard: Li Wei, Shen Shaojin, Jia Guangru, Li Shilei, Zhao Yuying, Zhang Zhongcheng, Wang Xutao, Wang Jiaqiang This standard is interpreted by the Environmental Protection Department of Hebei Province. Ultra-low emission standards for industrial air pollutants 1 Scope This standard specifies the ultra-low emission concentration limits of atmospheric pollutants in industrial sintering (pellets), blast furnace ironmaking, steel making, hot rolling and cold rolling production enterprises in Hebei Province, and clarifies the relevant provisions of sampling, monitoring and environmental protection management. This standard is applicable to the air pollutants of existing enterprises or production facilities in Hebei Province, as well as the environmental impact assessment of industrial construction projects, the design of environmental protection facilities, the completion of environmental protection acceptance and the discharge management of atmospheric pollutants after commissioning. This standard applies to the discharge of pollutants permitted by law. For pollutants that have been stipulated in this standard, pollutant discharge standards that are stricter than this standard may be implemented. 2 normative references The contents of this standard refer to the following documents or their terms. For dated references, only the dated date applies to this document. For undated references, the latest edition (including all amendments) applies to this document. GB/T15432 Determination of total suspended particulate matter in ambient air HJ836 Fixed pollution source, low concentration of particulate matter - Determination of gravimetric method Determination of particulate matter in GB/T16157 fixed pollution source exhaust gas and sampling method of gaseous pollutants HJ/T27 Determination of Hydrogen Chloride in Fixed Source Pollution Sources - Mercury Thiocyanate Spectrophotometry Determination of chromic acid mist in HJ/T29 fixed source exhaust gases - Diphenylcarbonyl hydrazide spectrophotometric method Determination of total hydrocarbons, methane and non-methane total hydrocarbons from fixed sources of HJ38 - Gas chromatography Determination of nitrogen oxides in HJ/T42 fixed pollution source - Ultraviolet spectrophotometric method Determination of nitrogen oxides in HJ/T43 fixed source s HJ/T55 Technical Guidelines for Unconserved Emission Monitoring of Air Pollutants Determination of sulfur dioxide in HJ/T56 fixed source exhaust gas - Iodometric method Determination of sulfur dioxide in HJ57 fixed pollution source - Determination of sulfur dioxide Determination of Fluoride in HJ/T67 Atmospheric Fixed Pollution Sources Ion Selective Electrode Method HJ75 fixed pollution source flue gas (SO2, NOX, particulate matter) continuous monitoring technical specifications HJ/T76 fixed pollution source flue gas emission continuous monitoring system technical requirements and testing methods (trial) HJ77.2 Determination of Dioxins in Ambient Air and Exhaust Gases - Isotope Dilution High Resolution Gas Chromatography - High Resolution Mass Spectrometry HJ/T397 fixed source exhaust gas monitoring technical specification HJ/T398 Fixed Pollution Sources - Determination of Smoke Blackness - Ringerman Smoke Blackness Diagram Determination of lead air in HJ539 - Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometric method Determination of sulfuric acid mist of HJ544 fixed pollution source - Ion chromatography Determination of hydrogen chloride in HJ548 fixed pollution source - Silver nitrate volumetric method HJ549 ambient air and exhaust gas - Determination of hydrogen chloride HJ583 Determination of Benzene in Ambient Air - Solid Adsorption / Thermal Desorption - Gas Chromatography HJ584 ambient air benzene series determination of activated carbon adsorption / carbon disulfide desorption - gas chromatography HJ629 - Determination of sulfur dioxide in fixed source pollution - Non-dispersive infrared absorption method Determination of nitrogen oxides of HJ692 fixed pollution source - Non-dispersive infrared absorption method Determination of nitrogen oxides in HJ693 fixed pollution source - Determination of potentiometric electrolysis DB13/T2589 Industrial Emission Soot Concentration Determination Method - Infrared Spectrophotometry Measures for the Automatic Monitoring and Control of Pollution Sources (Order No. 28 of the State Environmental Protection Administration) Measures for the Administration of Environmental Monitoring (Order No. 39 of the State Environmental Protection Administration) 3 terms and definitions The following terms and definitions apply to this standard. 3.1 Industry The industries referred to in this standard include sintering (pellets), blast furnace ironmaking, steel making, hot rolling and cold rolling production processes, excluding refractory materials, carbon products, coking and ferroalloy production. 3.2 Existing companies Before the date of implementation of this standard, the production enterprise or facility that has been approved for production or environmental impact assessment documents has been completed. 3.3 New enterprise From the date of implementation of this standard, the environmental impact assessment document will pass the examination and approval of new, modified or expanded production enterprises or facilities. 3.4 standard status Refers to the state of temperature 273.15K and pressure 101325Pa. 3.5 exhaust pipe height Refers to the height from the ground level where the exhaust cylinder (or its main building construction) is located to the outlet of the exhaust. 3.6 Continuous monitoring of flue gas emissions Refers to the continuous and real-time tracking and monitoring of flue gas discharged from fixed pollution sources, also known as online monitoring of flue gas emissions. 4 pollutant emission control requirements 4.1 Organized emission standards for atmospheric pollutant emissions The existing enterprises shall implement the emission limits specified in DB13/2169-2015 and the “Publication of Hebei Provincial Environmental Protection Agency on the Implementation of Special Emission Limits of Air Pollutants in Hebei Province†(No. 1 of 2016) before January 1, 2020 The emission limits specified in Tables 1 to 4 shall be implemented as of January 1, 2020. 4.2 Unorganized emission concentration limits Any one-hour average concentration of atmospheric pollutants at the enterprise boundary shall be subject to the limits specified in Table 5. Raw materials such as iron concentrates, coal, coke powder and other auxiliary materials are stored in closed material yards (bins, sheds, and warehouses), and dust suppression measures such as spraying are adopted. The dust points of the production units during loading, unloading, processing, storage and transportation of materials, sintering (pellet) equipment, iron tapping, main ditch, iron ditch, slag ditch, etc. of the iron-making iron field, and refinery pretreatment, The local gas collection system and the centralized purification treatment device must be set up in the production process of converters for iron, electric furnace feeding, slag discharge, tapping, etc., and the purified gas is discharged by the exhaust pipe. 4.3 If the production tail gas of the enterprise does need to be burned and discharged, the blackness of the smoked Ringermann shall not exceed 1 grade. 4.4 exhaust pipe (chimney) height requirements All exhaust cylinders should be at least 15m high. When there is a building within a radius of 200m around the exhaust pipe, the height of the exhaust pipe should be higher than the highest building by more than 3m. 4.5 The concentration of atmospheric pollutants in the measured exhaust pipe of steelmaking lime kiln, dolomite kiln and rolling steel heat treatment furnace shall be converted into the baseline emission concentration under the condition of 8% oxygen content according to formula (1), and use this as a judgment to determine whether the emission is up to standard. Basis. Before the national or provincial government has not specified the baseline exhaust gas volume of other production facilities, the measured concentration is used as the basis for determining whether the air pollutant discharge meets the standard. 5 pollutant monitoring requirements 5.1 Sampling of exhaust emissions from enterprises shall be carried out according to the type of pollutants to be monitored at the specified pollutant discharge monitoring position. If there is an exhaust gas treatment facility, it shall be monitored after the facility. A permanent identification shall be provided at the pollutant discharge monitoring location. 5.2 The requirements for the installation of automatic monitoring equipment for pollutant discharge by newly-built enterprises and existing enterprises shall be implemented in accordance with the relevant laws, regulations, technical specifications and the Measures for the Automatic Monitoring and Control of Pollution Sources. 5.3 The frequency of monitoring the emission of pollutants of enterprises, sampling time and other requirements shall be implemented in accordance with the State's relevant technical guidelines for pollution source monitoring. Sintering and electric furnace dioxin indicators are monitored once a year. 5.4 Monitoring and sampling of atmospheric pollutants in the exhaust pipe shall be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB/T16157 and HJ/T397. 5.5 The sampling points for unorganized emission of atmospheric pollutants in the plant are located at the discharge ports of doors, windows, roofs and gas buildings of the production plant, and the maximum concentration is selected. If the unorganized emission source is open-air or has no surrounding wall, the monitoring point should be selected at any point from the smoke (powder) dust emission source 5m, the lowest height of 1.5m, and select the maximum concentration. Sampling of unorganized emission monitoring points, using any continuous 1h sample average, or collecting 4 samples at equal time intervals within any 1h. 5.6 The enterprise shall monitor the sewage discharge status in accordance with the relevant laws and the “Measures for the Administration of Environmental Monitoring†and maintain the original monitoring records. 5.7 Monitoring of unorganized emissions of particulate matter in the plant (field) sector, and the monitoring method implements the provisions of the Technical Guidelines for Monitoring Unorganized Emissions of Air Pollutants (HJ/T55). 5.8 The determination of atmospheric pollutant emission concentrations is based on the method criteria listed in Table 6. 6 implementation and supervision 6.1 This standard is supervised and implemented by the environmental protection administrative department of the people's government at or above the county level. 6.2 Under any circumstance, the enterprise shall comply with the pollutant emission control requirements of this standard and take necessary measures to ensure the normal operation of the pollution prevention facilities. When the environmental protection departments at all levels conduct supervisory inspections on enterprises, they can use the results of on-site sampling or monitoring as the basis for determining whether the pollutant discharge behavior meets the emission standards and implements relevant environmental protection management measures. Bolts available from TS Hardware include a comprehensive range of threaded bolts, screws, studs and other essential components used for construction and industrial applications. We manufacture and supply bolts in an extensive selection of sizes, types and materials, including TC Bolts, sheer studs, self drilling screws, and more. We can provide our customers with virtually any type of bolt they need and serve as a one-stop-shop for construction and building components. Carbon Steel Bolt,High Carbon Steel Bolts,Carbon Steel Nuts,Carbon Steel Wedge Anchor Taizhou TS HARDWARE Co., Ltd , https://www.shuwengroup.com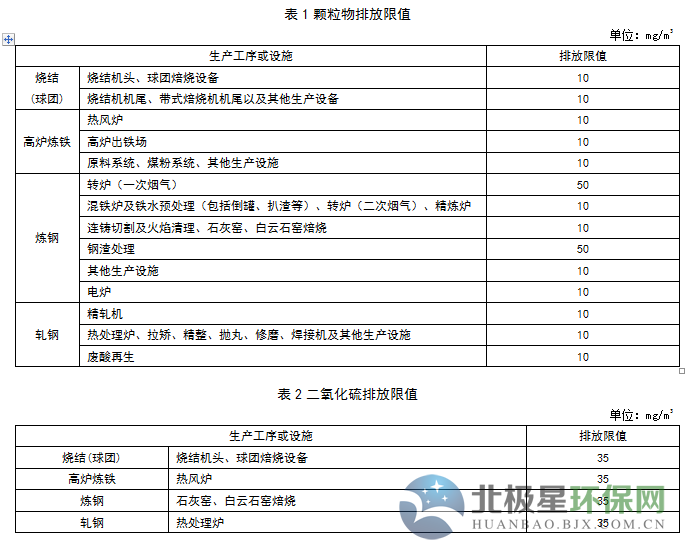




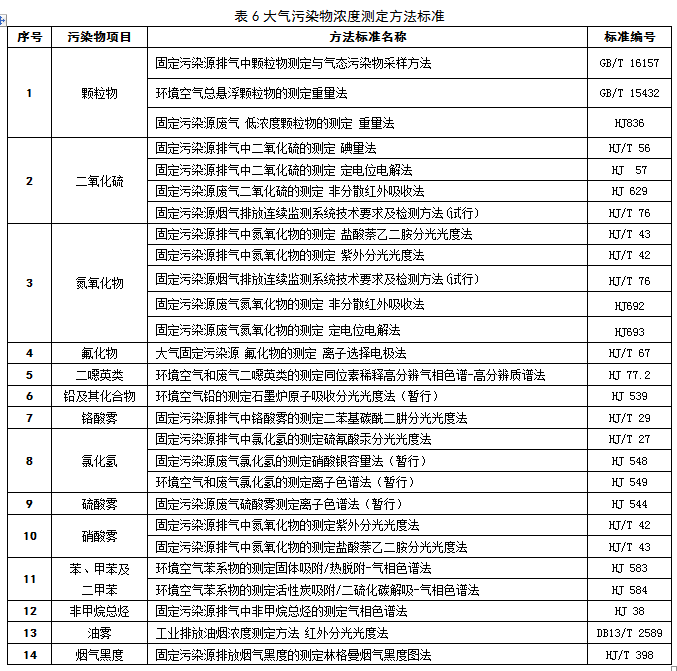
Hebei: Ultra-low emission standards for atmospheric pollutants in the steel industry (draft for comments)
/*kangxianyue 250*250 was created on 2017/3/29*/ var cpro_id = "u2939694";