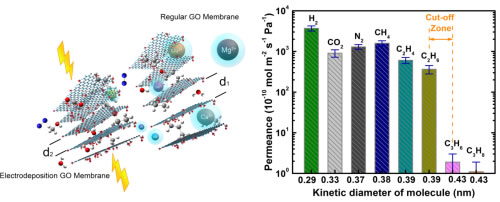
Recently, the Key Laboratory of Low Carbon Conversion Science and Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Shanghai High-Tech Research Institute-Shanghai University of Science and Technology Low Carbon Energy Joint Laboratory have made progress in the electrodeposition of graphene oxide composite membranes for accurate size screening. The related results were published in Nature Communications. Separation of mixtures is a highly energy-intensive process in industrial production. Membrane separation technology has the advantages of low energy consumption, high efficiency, and low cost. As an emerging membrane material, two-dimensional materials such as graphene oxide and its derivatives exhibit good separation performance in liquid-phase separations such as solvents and ions and gas separation, and have become one of the research hotspots in the field of membrane separation. However, how to precisely regulate (reduce) the two-dimensional interlayer spacing of graphene oxide to accommodate the efficient screening of molecules or ions of different sizes, and how to enhance the mechanical strength of graphene oxide, a flexible material, is extremely challenging in this field. Sexual problems. Based on previous work (Chem Commu, RSC Adv,), Zengfeng's research team has developed and validated a method for rapidly preparing ultra-thin graphene oxide composite films by electrodeposition on porous stainless steel hollow fibers. The two-dimensional layer spacing enhances the mechanical properties of the film. Under the action of an annular electric field, graphene oxide is first electro-reduced on the counter electrode, and then electrostatically forced to deposit on the working electrode stainless steel hollow fiber surface to form an ultra-thin uniform graphene oxide film. The electro-reduction can control the two-dimensional interlayer spacing of graphene oxide within a certain range, so that it can be applied to a specific separation system. It was found that the graphene oxide composite film obtained under optimized deposition conditions can accurately screen very similar sizes of C2 (ethane and ethylene) and C3 (propane and propylene) hydrocarbon molecules (Figure 1), C2/C3 The ideal selectivity is 190-550. The separation of C2 and C3 hydrocarbons has practical separation requirements in natural gas purification, MTO and FTO. In addition, electrodeposited graphene oxide composite membranes exhibit extremely high selectivity for separation in the liquid phase separation of alcohol dehydration and seawater desalination, enabling efficient screening of the smallest alcohol molecules and ions. The research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Bathroom Accessories Towel Rod Rack KaiPing HuiPu Shower Metalwork Industrial CO,LTD , https://www.hp-shower.com