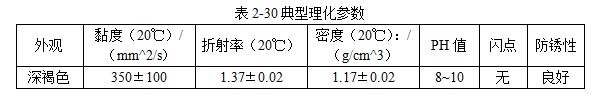
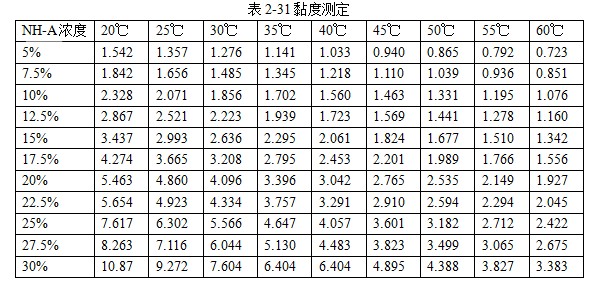
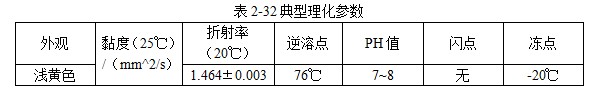
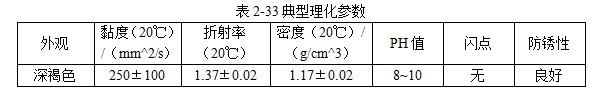
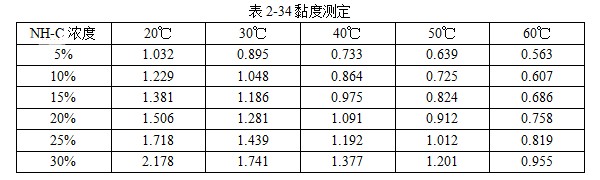
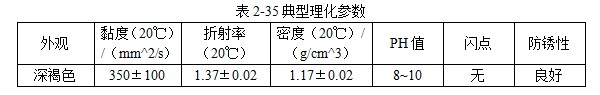
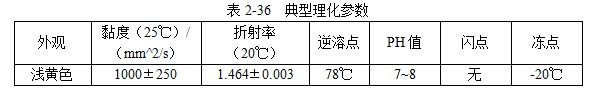
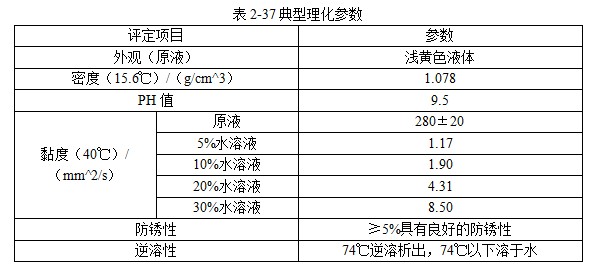
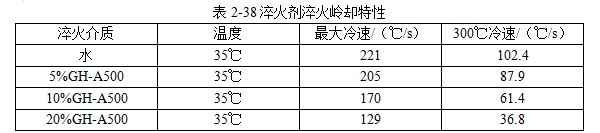
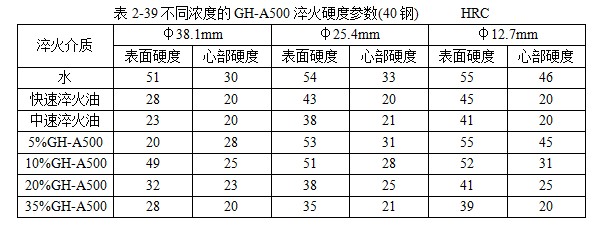
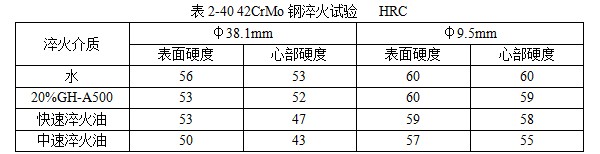
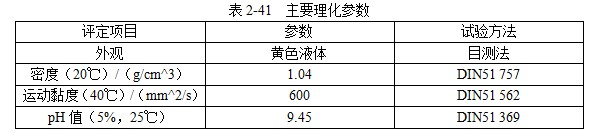
101 JEF-5.7 [Quenching and cooling characteristics] Same as 099 JEF-l. [Main use] Applicable steel grades 35 to 40, 30 to 35, and 20 to 30. The hardness can reach 52 ~ 57HRC, 40 ~ 52HRC, 27 ~ 42HRC. 102 former Soviet rocon-K quenching agent [Introduction] The former Soviet rocon-K quenching agent is a 50% aqueous solution of ethylated alkanol containing a foam-eliminating and anti-rust additive. [Main use] 10% ~ 65% of rocon-K quenching agent can be used for 45, 40X, 40XH2MA and other steel quenching. Under the premise of no cracking after the parts are quenched, the following concentration (mass fraction) aqueous solution can ensure the parts have high hardenability. Carbon steel: 0~30% rocon-K medium Alloy steel: 30% to 60% rocon-K medium. [Precautions for use] The quenching liquid temperature should not exceed 40 °C. 103 Daphne Plastic Quench RP ã€Introduction】 Daphne Plastic Quench RP, a medium-sized water-soluble quenching liquid suitable for quenching, rust-proof and anti-corrosion, from quenching to high-frequency quenching. Applicable oil temperature: 30 ~ 60 ° C, the medium has good cooling and brightness, can reduce deformation, prevent cracking, and better rust resistance. Moreover, by comparing between cold oil, neutral oil and hot oil, the characteristic results of the water-soluble quenching liquid are shown. [Main use] High-frequency quenching of engine parts, quenching and tempering of running parts of automobiles, trucks, and construction machinery. 104 NHA quenching agent [Introduction] The quenching medium is a non-oil-soluble viscous liquid synthesized from a variety of high molecular polymers and additives. It is infinitely interlocked with water and has no reverse solubility. The medium is properly formulated by different organic substances and additives, so that the temperature of the quenching liquid rises and the cooling performance is relatively stable. By adjusting the concentration of its use, a cooling medium with a cooling capacity from brine to oil can be obtained. There is no oil smoke pollution during quenching, and the workpiece does not need to be cleaned after quenching with low concentration medium. Long-term use does not require a full tank replacement. [Typical physical and chemical properties] The typical physical and chemical parameters are shown in Table 2-30. [Quenching and cooling characteristics] When the red hot workpiece is quenched into the medium, a very thin film of colloidal film is gradually formed on the surface of the workpiece to slow the conduction of heat from the workpiece to the solution, so that the workpiece avoids excessive thermal stress. Small quenching deformation. For workpieces of different materials and shapes, by adjusting the medium concentration, the quenching deformation can be reduced and quenching and cracking can be avoided. The medium has a wide temperature range of use. The quenching of carbon steel and alloy steel workpieces is insensitive to small changes in the cooling capacity of the medium due to the low thermal conductivity of the steel. The medium increases with the use temperature and the mechanics of the workpiece after quenching. Performance has little effect. ã€The main purpose】 1 The quenching boat cooling capacity changes with the adjustment of the concentration. It can be used for the quenching of 45 steel dangerous workpieces, the quenching of low-alloy steel workpieces such as medium and large size 40Cr, and the carburizing quenching of low carbon steel workpieces such as 20Cr. 2 has been widely used in large-scale quenching of hand tools, automotive parts and the like. 3 For the quenching of the workpiece heated by the salt bath furnace, the quenching of the continuous thin layer of carburized parts, and the quenching of the periodic carburized workpiece. [Media Maintenance] During the use of the medium, there is inevitably a phenomenon of water evaporation and belt consumption, which causes changes in the medium concentration, and is used in daily use. The concentration of the polymer quenching medium should be checked regularly. And timely adjustment, the detection method can be selected according to the requirements of the quenching workpiece on the cooling performance of the polymer quenching medium in different temperature ranges. (1) Viscosity hazard size The overall quenching of carbon steel or low-alloy steel workpieces, in order to prevent quenching cracking, quenching deformation is too poor, the viscosity of the quenching medium should be measured regularly, please refer to GB 265 for the determination method. The viscosity results are shown in Table 2-31. (2) Refractive index Within a certain range, there is a linear correspondence between the refractive index and the concentration of the quenching medium of the polymer. It is very simple to measure the quenching medium on site by using a sugar meter. The amount of sugar count directly reflects the cooling capacity of the polymer quenching medium in the first and second stages of cooling, the overall quenching of the carbon steel workpiece or the surface quenching of the carbon steel and low alloy steel workpiece, and the reading of the quenching medium sugar meter The control can effectively ensure the quenching performance of the workpiece. C%=K§% (C: medium concentration, K: coefficient, §: sugar meter reading) K = 3.53 (20 ° C) In actual production, because the refractive index is affected by factors such as the quenching of the workpiece into the scale, it is necessary to correct the K value frequently, and correct the K value by combining the test results of the cooling curve, viscosity and density. (3) The density is within a certain range, and there is a linear correspondence between the density and the concentration of the quenching medium. It is also convenient to use the density meter to measure the quenching medium on site. C%=G&% Where C is the medium concentration; G - coefficient, G = 28.3 (20 ° C); & - Densitometer reading. In actual production, the G value is also often corrected, and the correction method is similar to the K value correction. 105 NH-B quenching agent [Introduction] The polymer NH-B quenching medium is a polyglycol polymer quenched boat with anionic linear structure by catalytic copolymerization of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide. The quenching medium is a non-oil-soluble viscous liquid which is infinitely miscible with water and has reverse solubility. Appearance is milky white to light yellow viscous liquid, stable performance, easy to test, recyclable and reusable. By adjusting the concentration of its use, a cooling medium with a cooling capacity from water to oil can be obtained. There is no oil smoke pollution during quenching, and the workpiece does not need to be cleaned after quenching with low concentration medium. The medium and the imported polyglycol quenching medium are similar products, and the performance indexes are similar and can be mixed with each other; for the quenching tank which has used the imported medium, the medium can be gradually added during use instead of the imported polyglycol to reduce the cost. [Typical physical and chemical properties] The typical physical and chemical parameters are shown in Table 2-32. [Quenching and cooling characteristics] NH-B water-soluble quenching medium has reverse solubility. When a certain concentration of uniform aqueous solution cools the high temperature workpiece, the solution near the surface of the workpiece quickly reaches the reverse dissolution temperature, and the flocculent polymer is precipitated. The polymer adheres to the surface of the workpiece to form a polymer separator; the higher the concentration of the medium, the greater the thickness of the separator. The thermal barrier of the separator slows down the cooling rate of the medium. Therefore, by controlling the concentration of the medium used, a cooling medium having a cooling capacity from water to oil can be obtained. The separator formed on the surface of the workpiece during quenching can slow down the convective cooling of the medium to the workpiece. Therefore, the medium cools smoothly during the low-temperature cooling phase, reduces the structural stress generated by the martensitic transformation, and avoids the occurrence of quenching cracks. The cooling curve and characteristic curve of the medium change smoothly within a certain range, which indicates that during the production process, the concentration has a little influence on the quenching effect when it fluctuates within a certain range. ã€The main purpose】 The 1NH-B medium has stable cooling performance and can be used as a substitute for quenching oil for quenching of small-sized carbon steel and low-alloy steel. 2 Instead of hot water for the quenching of aluminum alloy, avoid quenching soot, fire hazard, improve the comprehensive mechanical properties of the workpiece after quenching. [ routine maintenance] (1) Determination of concentration using NH-B quenching medium is simple and can be directly reflected by the reading of the sugar meter (except for the quenching medium sold by adding water). The medium that has been used for a long time should be combined with viscosity, density and cooling curve. The correction factor K is corrected. Within a certain range, there is a linear correspondence between the refractive index and the concentration of the quenching medium of the polymer. The quenching medium is conveniently measured in the field by a sugar meter. The amount of sugar count directly reflects the cooling capacity of the polymer quenching medium in the first and second stages of cooling, and the reading of the NH-B quenching medium sugar meter is the concentration of the quenching medium. C%=K§% Where C is the medium concentration; K - coefficient, K = 1.0 (20 ° C); § - Sugar meter reading. In actual production, it is affected by factors such as the quenching of the workpiece into the scale, and the K value needs to be corrected frequently. (2) Medium recovery High-alloy steel and aluminum alloy quenching using high-concentration NH-B medium, the liquid containing NH-B medium after cleaning the workpiece, heated to above the reverse dissolution temperature, releasing the above clear water, the following concentrated liquid Can be used for the addition of media. For the salt-containing medium and the medium which has been used for a long time, the liquid may be layered, the salt-containing water is removed, and impurities such as the bottom oxide scale are filtered to obtain a viscous NH-B quenching medium. 106NH-C quenching agent [Introduction] Same as 104 NH-A quenching agent. [Typical physical and chemical properties] The typical physical and chemical parameters are shown in Table 2-33. [Main use] It can replace quenching medium such as CaCl2 and trinitrate for quenching of large-size carbon-copper forgings. [ routine maintenance] (1) Viscosity For quenching of easily cracked workpieces, the viscosity of the quenching medium should be measured periodically. See Table 2-34. (2) Refractive index The NH-C polymer quenching agent is used in the refractive index to determine the concentration of the hardened layer of the blank. C%=K§% Where C is the medium concentration; K - coefficient, K = 3.75 (20 ° C); § - Sugar meter reading. (3) Density C%=G&% Where C is the medium concentration; G - coefficient, G = 28.35 (20 ° C); & - Densitometer reading. 107NH-D quenching agent [Introduction] Same as 104 NH-A quenching agent. [Typical physical and chemical properties] The typical physical and chemical parameters are shown in Table 2-35. ã€The main purpose】 (1) Jet quenching using a polymer NH-D quenching medium, using a concentration range of 3% to 10%. (2) It can replace the quenching medium such as water and brine, and is used for induction heating spray quenching of carbon steel and low alloy steel workpieces to avoid corrosion of quenching injection mechanism and workpiece. [ routine maintenance] (1) Viscosity See NH-C polymer quenching agent. (2) refractive index C% = K§% Where C is the medium concentration; K - coefficient, K = 3.53 (20 ° C, NH-D); § - Sugar meter reading. (3) Density C%=G&% Where C is the medium concentration; G - coefficient, G = 28.3 (20 ° C, NH-D); & - Densitometer reading. 108 NH-E quenching agent [Introduction] Same as 104 NH-A quenching agent. [Typical physical and chemical properties] The typical physical and chemical parameters are shown in Table 2-36. ã€The main purpose】 1 It is used for induction heating and quenching of alloy steel workpieces with uniform surface hardness, avoiding the appearance of micro-cracks and reducing quenching deformation. The concentration (mass fraction) used ranges from 3% to 8%. 2 can replace water, oil and other quenching media, for induction heating spray quenching and wetting and quenching of medium and low alloy steel workpieces. [ routine maintenance] Refractive index is used to assess the concentration of the NH-E quenching medium sugar meter reading, which is the concentration of NH-E quenching medium. C%=K§% Where C is the medium concentration; K - coefficient, K = 1.0 (20 ° C); § - Sugar meter reading. 109 JiChuan A and Jichuan E quenching agent [Introduction] It is a non-combustible water-soluble polymer quenching agent composed of a liquid organic polymer and a corrosion inhibitor. The organic polymer is completely soluble in water to form a clear, homogeneous aqueous solution. However, when the temperature exceeds 74 ° C, the polymer separates out from the water to form an insoluble phase. The media requires a minimum amount of replacement because they are less susceptible to deterioration than conventional polyvinyl alcohol and dissolved oil. [Quenching and Cooling Characteristics] When quenching with a dilute solution of the medium, a liquid organic polymer is deposited on the surface of the genus to form a film. The degree of cooling of the metal can be adjusted by adjusting the thickness of the film. The thickness of the film is achieved by adjusting the concentration of the medium in the quenching bath. Cooling can also be controlled by adjusting the temperature or agitation of the quenching liquid. By the method of controlling the above parameters, effects similar to those of cooling with oily quenching oil can be obtained. ã€The main purpose】 1 Large alloy steel workpiece for trolley furnace and pit furnace processing. 2 For processing parts (intermittent and continuous operation) requiring quenching liquid in the use of methane and carburizing nitriding furnaces. 3 Forging directly quenched parts. 4 high frequency or medium frequency induction heat treatment of various workpieces. 5 precipitation hardening heat treatment of aluminum alloy, forging, casting, solid solution and age hardening treatment. 6 continuous mesh belt furnace, multi-purpose box furnace, well furnace, trolley furnace and so on. 7 carburizing, nitriding, carbonitriding, quenching and tempering of endothermic or exothermic furnaces. 110 polyether·ethylene glycol aqueous solution [Introduction] Polyether·glycol sulphate can be formulated into aqueous solutions of various concentrations in a ratio of 1:1. The addition of ethylene glycol to the polyether reduces the cost of the quenching liquid and improves the surface finish. After quenching, the surface of the part is silver-gray, and the hardness is uniform, and 7 good effects are obtained in production. [Quenching and Cooling Characteristics] The maximum cooling rate of a solution having a concentration of 16% is 600 ° C / s, which is about 200 ° C. ã€The main purpose】 1 The quenching medium with a concentration of 16% to 20% is suitable for quenching of carbon tool copper, medium carbon structural steel, and spring steel. 2 can be used for quenching of box furnaces, salt bath furnace heating parts and induction heating parts. 111 GH-A500 [Introduction] Polyalkylene glycol-based polymer compounds have anti-rust properties, contain various additives such as anti-rust, anti-corrosion, wetting, sterilization, etc., and are oil-free, non-toxic and non-polluting. By adjusting the concentration of the medium, different cooling rates can be obtained, and the application range is wide; the hardened layer is deep, the quenching hardness is uniform, the no-point, the quenching deformation and the cracking tendency are small; the quenched workpiece is bright and has a short-term anti-rust effect, and can be cleaned. Direct tempering; no corrosion to ferrous and non-ferrous metals; not easy to age and deteriorate, long service life; less out-of-charge, low cost, high cost performance; no burning, no fire hazard, improve working environment. [Typical physical and chemical properties] The typical physical and chemical parameters are shown in Table 2-37. [Quenching and cooling characteristics] The quenching and cooling characteristics are shown in Table 2-38. The chilling speed of the GH-A500 in the convection stage is significantly lower than that of water, which greatly reduces the deformation and cracking tendency of the parts. See Table 2-39 and Table 2-40 for the quenching and cooling capacity of different concentrations of GH-A500. ã€The main purpose】 1 Suitable for heat treatment of carbon steel, alloy steel and cast iron: different concentrations are selected according to different carbon content and alloy composition, different performance requirements and different size of parts, generally between 5% and 25%. 2 induction hardening: quenching gears or camshaft parts that use induction heating or flame heating and oil cooling. This medium is the ideal substitute for quenching oil, completely eliminating oil smoke and fire hazards. 3 large parts of quenching: according to the carbon content, alloying elements and content, performance requirements, parts of different sizes and different concentrations, generally between 10% to 20%. 4 aluminum alloy solution treatment: common concentration is between 5% and 10%. 5 It is generally not recommended to use GH-A500 medium for quenching in a salt bath furnace. [Precautions for use] (1) Concentration detection The concentration of GH-A500 can be measured by a refractometer at the production site. Concentration % = Refractometer display reading × refractive index (new liquid is 2.5) During the use of the quenching liquid, the refractive index will be affected by the influence of system pollution. To ensure good control of the bath concentration, the medium should be sampled periodically to correct the on-site concentration value. (2) Temperature control The recommended optimum solution temperature is 20 to 40 ° C, but should be ≤ 55 ° C. It is recommended to control the quenching temperature to the narrowest possible range. The temperature rise before and after quenching of the bath is also controlled within 10 °C as much as possible, so a cooling cycle device is recommended. If the room temperature is too low in winter, consider heating the bath before quenching or increase the concentration appropriately. (3) Stirring control In order to obtain the quenching and cooling effect as uniform as possible, the bath should be continuously stirred. Pump circulation, propeller agitation and nozzles can be used, depending on the site. (4) Considerations In the production site, the steel type, shape complexity, size, heat treatment requirements and cooling system of the workshop can be considered comprehensively. 112 å¾·æ¶¦å® AQUATENSID [Introduction] Shanghai Derunbao Company water-soluble quenching solution. In the dip quenching, it is mainly used for the quenching of quenched and tempered steel and the heat treatment process of induction quenching and flame quenching. ã€The main purpose】 1 In the dip quenching, it is mainly used for quenching and quenching of quenched and tempered steel and heat treatment of flame quenching. 2 It is used for quenching aluminum parts, which can achieve the effect of no deformation or minimal deformation. 3 Quenching of alloy steel workpieces with good hardenability. 113 water-based quenching liquid 2000 [Introduction] The water-based quenching liquid PETROFER FERO-QUENCH 2000 introduced by Derunbao Company has similar cooling performance to quenching oil. The quenching liquid greatly broadens the application range of the water-based quenching medium, and does not generate smoke pollution during quenching, and avoids the hazard of fire, and can completely ensure the safety of operators and equipment. Contains no harmful substances such as mineral oil or nitrite. Due to the short vapor phase of the quenching liquid, different parts of the workpiece can be rapidly and rapidly entered into the boiling cooling process and a higher quenching cooling rate is formed; while in the low temperature stage of the cooling process (ie, the convection cooling stage), cooling is performed. It is very gentle, reduces the martensitic transformation microstructure stress, and greatly reduces the risk of quenching deformation and cracking of the workpiece. [Typical physical and chemical properties] The main physical and chemical parameters are shown in Table 2-41. ã€The main purpose】 1 Suitable for materials with good hardenability. In actual use, the concentration range is generally 10% to 20%, and most of them are used in the range of 15% to 20%. 2 It is suitable for large casting and forging of high alloy structure copper 40CrNiMo and 40CrMnMo, high strength steel pipe. 3 Suitable for high-carbon, high-manganese high-speed rail materials and some high-alloy touch steels like P20 and H13. 4 It is also possible to replace the mineral-based quenching oil which is prone to fire and smoke pollution at a suitable concentration, and perform heat treatment quenching cooling or controlled cooling. [Precautions for use] 1 The use temperature of the quenching liquid is generally in the range of 35 to 50 °C. In order to reduce the quenching speed, it can also be used up to 60 to 70 °C. The temperature rise of the liquid temperature is generally allowed to be 10 to 15 °C. For materials with good hardenability, the temperature of the quenching liquid should not be lower than 35 °C, because the quenching cooling rate, especially the low temperature stage, will be significantly accelerated. For materials with poor hardenability, the initial liquid temperature can be used even at temperatures as low as 10 °C. 2 In order to ensure the continuous and stable cooling performance of the quenching liquid, it is recommended that the concentration range of the quenching liquid concentration in normal use should not exceed +1%. For the long-term use of the quenching liquid, the viscosity method must be used to measure the concentration. Due to the large amount of evaporation of tap water, the accumulation of residual salt, impurities, and various external pollution (soluble matter) increase the refractive index of the solution. Therefore, the refractive index measured by the refractometer is used. A concentration curve calculates the concentration and there is a large concentration error. The concentration measured by the viscosity method can accurately measure the composition of the effective polymer in the quenching liquid. It is recommended to measure the concentration of the quenching liquid using the viscosity method. Daily measurements in production can be measured using a refractometer, but the refractive readings must be corrected for the quench concentration values ​​corresponding to the most recently measured viscosity. It is recommended to use a capillary viscometer with special motion viscosity measurement, which is suitable for measuring the viscosity value of 3~10mm^2/s (20°C) precision and range. The range of the refractometer is preferably 0 to 5 or 0 to 10. The refraction multiplication coefficient of the new quenching liquid is 5.25. That is, the new quenching liquid concentration = 5.25 × refractive reading. The longer the usage time, the greater the change (decrease) of this coefficient. 3 For some high-grade gold steel materials or parts that are easy to be quenched, it is recommended to discharge the liquid before the workpiece is cooled to liquid temperature to reduce the quenching stress and prevent cracking. 114 water-based quenching liquid SZ [Introduction] Derunbao water-based quenching liquid SZ, a viscous, non-toxic, light yellow liquid, is a polyalkylene glycol quenching agent with reverse solubility. It does not contain nitrite (carcinogens) or any other harmful substances. SZ quenching fluid has excellent rust prevention effect. However, if the concentration is low, the user needs to take special anti-rust measures. 0.2% to 0.5% anti-rust agent M503 can be added to the quenching liquid to improve the anti-rust effect of the solution. [Typical physical and chemical properties] The typical physical and chemical parameters are shown in Table 2-42. 5% or so low concentration SZ quenching liquid has excellent wettability to red hot metal. When the workpiece is immersed in the quenching liquid, the surface of the workpiece will quickly adhere to the desolvated polymer film, and the film can effectively destroy the vapor film formed on the workpiece by the water, thereby increasing the high temperature and cooling rate of the water, and cooling the different parts of the workpiece. Evenly. When the temperature of the workpiece is tempered to room temperature, the polymer will be re-dissolved, so it consumes little and can be used repeatedly. It only needs to be added normally and not replaced by the whole tank. ã€The main purpose】 1 Carbon structural steel and low alloy structural steel such as 45, 40Cr, 40MnB, 40Mn2 and other materials by induction or flame heating spray quenching, solve the use of tap water cooling, prone to quenching and quenching soft spots, using polyvinyl alcohol solution, However, there are many problems such as perishable agglomerates blocking nozzle holes, stinking, short effective life, poor concentration and control, and difficulty in ensuring stable quenching quality. 2 Replacement of tap water, salt (alkali) liquid, martensite quenching of low-carbon low- and medium-alloy steels, and quenching and tempering of carbon structural steels, currently widely used in dip quenching of standard parts and some forged blanks cool down. 5%~10% SZ quenching liquid is used for quenching and cooling workpieces with poor quenching carbon steel such as 45, 40Cr and other materials. 10%~20% SZ quenching liquid can be used for quenching and quenching of better hardenable structural steels such as 40Cr, 35CrMo, 42CrMo and 40MnB, which can obtain stable quenching quality and can replace quenching oil and perishable polyethylene. Alcohol quenching liquid. [Main use] It is an excellent induction, flame heating spray quenching medium. It is suitable for induction or flame heating spray quenching of carbon structural steel and low alloy structural steel such as 45, 40Cr, 413MnB, 40Mn2. [Precautions for use] 1 Concentration selection: Under normal circumstances, the better the hardenability of the material, the smaller the effective thickness of the workpiece, and the more complicated the shape, the higher the concentration used. 2 Preparation: Mix the concentrated solution of water-based quenching liquid SZ with tap water according to the ratio (mass or volume percentage), and there is no special requirement for the hardness of water. 3 Concentration check: Using a hand-held refractometer, the reading is measured, and the coefficient multiplied by 2.0 is the percentage concentration of the quenching liquid. 4 liquid temperature control: the best working temperature should be between 20 ~ 50 °C. If the temperature of the quenching liquid exceeds 60 ° C, it should be cooled to 40 ° C before the next batch of workpieces can be quenched and cooled. 115 water-based quenching liquid BW [Introduction] Derunbao water-based quenching liquid BW is a viscous, non-toxic green solution, which does not contain mineral oil, nitrite or any other harmful substances. The concentrate is diluted with water and used. By formulating solutions of different concentrations. A quenching cooling rate that is faster than oil but slower than water is obtained. When carbon steel and low alloy steel are quenched, they must be cooled quickly and uniformly, requiring a very short vapor phase of the quenching liquid. A low concentration of aqueous quenching liquid BW can meet the above requirements. When the alloy steel is quenched with water, it is easy to be quenched due to good hardenability. Quenching oil can hardly be used for induction quenching of induction hardeners. In order to avoid deformation and cracking of the parts, a high concentration of Derunbao water-based quenching liquid BW can be used to reduce the quenching cooling rate of the water. ã€The main purpose】 1 The medium is widely used for dip quenching, such as direct quenching of forgings from forging temperatures, quenching of hand tools and agricultural machinery parts. 2 After carburizing and nitriding the workpiece, according to the difference of the shape of the workpiece, quenching in 5%~12% of Derunbao water-based quenching liquid BW, for quenching of open quenching tank and continuous furnace workpiece Good results. 3 Carbon steel recommended concentration: carbon content (mass percentage)>0.30%~0.50%, concentration 3%~8%; carbon content>0.50%~0.70%, concentration 10%~15%. 4 alloy steel (alloy steel containing chromium, molybdenum, vanadium) has a carbon content of >0.30% to 0.50%, and the recommended concentration is 12% to 25%. 5 For the spray quenching of induction quenching agent, the concentration is 3% to 5%. 6 During the immersion quenching, the optimum working temperature of the quenching liquid is 25 to 45 °C. The temperature for the induction hardener is generally 25 to 35 ° C and the highest is 50 ° C. The temperature of the quenching liquid should never exceed 60 °C. If the temperature of the quenching liquid exceeds 60 ° C, it should be cooled to below 40 ° C to quench the next batch of workpieces. [Precautions for use] 1 The method of checking the concentration is very simple, just use the hand-held refractometer to measure the refractive index of the solution at the site of use. 2 When the medium is used for dip quenching for a long time, it is recommended to check the viscosity of the solution at 20 °C frequently. Because the consistency between the viscosity and quenching cooling characteristics is closer than the refractive reading and cooling characteristics. Refractive readings are affected by impurities in the solution, while viscosity is not affected. 3 The medium generally does not foam. If there is a foam, please find the cause. Consider whether the pump is in the air or whether the liquid return pipe is not buried under the liquid surface. 4 Under normal circumstances, the medium can provide sufficient anti-rust effect, but if the use concentration is low, and the user requires special anti-rust effect, 0.2% to 0.5% anti-rust agent M503 can be added to the quenching liquid to Improve the rust prevention effect of the solution. 5 The water-based quenching liquid Bw concentrate is uniformly mixed with water, and then used as a solution having a certain concentration. There is no special requirement for the hardness of the water during the arrangement. 116 water-based quenching liquid JX For its characteristics and uses, please refer to 115 water-based quenching liquid Bw. 117 QT quenching agent [Introduction] Lianchuang QT type quenching agent is a new type of organic polymer quenching agent. The quenching agent is non-toxic, odorless and non-combustible. Its cooling performance varies widely. The variable cooling rate ranges from water to oil. Between, close to oil, slower than oil. Has a strong adaptability. The quenching agent has a low concentration, generally between 1% and 6%, and the amount of workpieces taken out is small, which reduces the production cost. The quenching agent is highly resistant to spoilage and does not spoil for several years during storage. The medium can be used to monitor the solution concentration using an Abbe refractometer, and the temperature range is 15 to 55 °C. [Typical physical and chemical properties] Appearance: brown yellow transparent viscous liquid Viscosity: 40 ~ 65s (coating a l viscosity meter) Density / (g / cm ^ 3): 1.090 pH: 7-8 ã€The main purpose】 1 Mainly used for quenching and quenching of medium carbon alloy steel such as 45, 40Cr and 35CrMo steel. 2 A forging factory produces the front axle of the car. The forging material is 40Cr and weighs about 47kg. Oil quenching is not hard, water quenching cracks, and the cracking rate has been as high as 50% or more. QT quenching liquid is used, the concentration is 2% to 3%, and the daily production is about 180 pieces. The continuous production for more than 8 years has no cracking and scrapping, and the quality is all qualified. 3 The automobile steering knuckle produced by a forging factory, the material is 40Cr, the water quenching is obvious, and the QT type quenching liquid is used. No cracking and good quality. 118 patent water-soluble quenching agent [Introduction] The water-soluble quenching medium is composed of an appropriate amount of a polyether polymer mixture, a surfactant, an inorganic salt, a bactericide, an inorganic base, and tap water. It has the advantages of low concentration, long life and stable quenching quality. Quenching agent composition: the solution has a molecular weight of 4000 to 15000 polyether (mass fraction) of 45% to 55%, a surfactant of 0.05% to 0.1%, an inorganic salt of 0 to 2.0%, and an inorganic base of 0 to 0.6%. The rest is tap water. ã€The main purpose】 1 The quenching medium of the patent can be used for the overall quenching of carbon steel at a concentration (mass fraction) of 4% to 6%. A concentration of 28% to 12% (mass fraction) can be used for high frequency quenching of carbon steel. 119 XL-Zinc Chloride Water Soluble Quenching Agent [Introduction] XL is mainly a derivative of alkylbenzene, which has high oxidation resistance and thermal stability. It is a brown viscous liquid with a relative density of 1.5. When used in water, it can be used in combination with zinc chloride (additional salts are not as effective as zinc chloride). Zinc chloride can destroy the vapor film on the working surface, increase the characteristic temperature of the medium, shorten the time of the vapor film stage, and increase the ridge velocity in the quenching critical region. In the late stage of the boiling phase, the viscosity increases and the surface of the workpiece is continuously quenched. The resulting deposits slow down the heat transfer and reduce the cooling rate, thereby reducing the stress in the quenching part, preventing cracking and reducing the amount of deformation. [Main use] It can be used for quenching cooling of 45 steel and GCrl5 steel. 120"511" water-soluble quenching agent [Introduction] The medium is non-toxic, odorless, and has good rust-preventing properties. It has less foaming and good corrosion resistance. After quenching, the hardness and metallographic structure of the heat-treated parts are qualified. It is mainly composed of high-molecular organic polymer, and has a quenching high-temperature zone cooling rate adjusting agent, which can be mutually miscible with water in any ratio, and the cooling rate can be adjusted. [Main use] It can be used for induction impregnation, carbon steel, alloy structural steel and bearing steel. 121 Russian water quenching agent [Introduction] Patent No.: 72458l and 1061457. The quenching medium is not inferior to mineral oil in terms of durability and smelting metal quality, and it exceeds other known media based on water-based polymers such as sodium polyacrylate, polyethylene alcohol, etc. . The medium processing initial temperature is wide: 4 to 80 °C. The cooling capacity was monitored by varying the polymer concentration and adding sodium chloride or other salts and stirring. This can be adapted to all types of steel, all possible sizes and shapes. The medium quenching tank is 4 times longer than the oil quenching tank. The quenching medium does not burn the surface of the product during the smelting process, the medium has no fire hazard, is non-toxic, and does not pollute the environment. It does not cause difficulties in the efficient use of processing fluids. [Main use] This quenching medium is widely used in Russia for hot-worked metal alloy products, structural steels and special purpose pig iron. 122NQ water-soluble quenching agent [Introduction] It has adjustable cooling speed and good quenching effect. By adjusting the concentration of quenching liquid and quenching temperature, the parts are not cracked and the quenching deformation is reduced. Stable cooling performance, no burning, no smoke in quenching, no fire hazard; non-toxic, non-polluting environment; neutral, non-corrosive parts and quenching tank and cooling system. The surface of the quenched part is clean and can be directly tempered without cleaning. When replacing oil quenching, the hardenability and hardenability of the parts are higher than the oil quenching effect, no risk of cracking; less quenching consumption and low cost; anti-aging, long-term use without deterioration, no odor, simple preparation and maintenance. ã€The main purpose】 1 Widely used in immersion quenching and spray quenching of metal products such as carbon steel, alloy steel, cast iron and non-ferrous metals to replace other types of water-soluble quenching media. 2 The medium has been applied in various industries such as tools, automobiles, and molds. 3 In practical applications, the medium oil tank (50 ~ 100t) quenching was successfully replaced by this medium. 123 anionic poly soap aqueous solution [Introduction] It is a polyacrylate type. An anionic poly soap having a molecular weight of 25,000 to 40,000 can be used as a solute. If the molecular weight exceeds the upper limit, the vapor film phase tends to prolong; when the molecular weight exceeds the lower limit, the workpiece rapidly cools below the Ms point. In actual use, acrylamide type, polyethylene lead chloride type, calcium chloride, ferrous oxide, etc. are used as a coagulating agent, and the COD value of the 10% anionic poly soap aqueous solution can be determined by the agglutination salting out method. ×10^-6 is reduced to 60×10^-6 to increase toxicity. [Quenching and cooling characteristics] Compounds formed by decomposition of polymers at the start of cooling The transition temperature in the aqueous polymer solution is slightly lower; the steel quenched into the lead bath has a slightly higher cooling rate over the entire transition temperature range than the quenched polymer aqueous solution. The total (over-co-precipitation) steel bar is quenched into 30% to 40% of Aguaquench110 quenching medium to obtain fine flaky pearlite; when the temperature is 90 ° C, it is carried out in 30% to 40% Aguaquenchll0 quenching medium. The mechanical properties of the toughened steel bars are generally between air cooling and lead bath treatment. In parts for larger sizes (≥4~5mm), the swinging effect is small, which is beneficial to the stability of the vapor film, thus reducing or reducing the towing loss and toxicity problems. The polyacrylate film formed on the surface of the workpiece can be completely burned when tempered at 472 ° C or higher, and can be washed with water before tempering at 472 ° C or lower. [Main use] It can be used to toughen the wire. 125 original Democratic German patent emulsion [Introduction] Patent No.: No67900, published day 1969.7.20. The emulsion medium is composed of 20% to 35% Na2Si04, 1% KOH, 1% fatty acid, 1.5% refined lubricating oil, and 100% water. Its cooling rate is between water and oil. [Main use] The medium is cheap and mostly used to replace the water quenching oil cold medium. 126 69-1 emulsified oil fire liquid [Introduction] When the emulsified oil is added to water, the cooling rate can be lowered, the stability of the vapor film can be improved, and the boiling phase can be transferred to the low temperature region. The emulsified quenching liquid is not easy to deteriorate and smell, and has a long service life and good anti-pound property. Quenching agent composition: first dissolve the emulsified oil with a small amount of water (about 40 ° C). Then, it is diluted with water at room temperature to a desired concentration (mass fraction) of 10% to 15%. The emulsified quenching oil can be used in an aqueous solution having a concentration (mass fraction) of 1% to 5%. [Main use] It can be used for induction heating quenching of medium carbon steel. The use temperature is 20 to 45 °C. 127 water oil opaque medium [Introduction] Emulsion consists of a mixture of liquid or emulsion with a non-common liquid. Water oil emulsions have less resistance to delamination. When a small amount of oxidatively polarized vegetable oil or other stabilizer is added, the delamination stability is slightly improved. The uniformity of cooling of the emulsion is poor. When the workpiece is subjected to integral heating and quenching, the hardenability and hardness are not uniform, deformation and cracking are easy to occur, and the cooling rate is greatly affected by temperature. [Quenching and cooling characteristics] When quenching with emulsion, the cooling of the film boiling zone is slow in the high temperature and medium temperature zones. In the low temperature zone, the cooling capacity of the emulsion increases with the increase of oil content from 3% to 20%. When the oil content is increased again, the cooling capacity is reduced. [Main use] Only for spray cooling. Drop Cloth,Plastic And Cotton Drop Cloth,cotton drop cloth PRO-CHARGER CO., LTD. (VICTOR HERO HOLDINGS LTD, TIME VALUE LTD.) , https://www.pro-chargerco.com